Repo Rate Reduction : RBI Cuts Repo Rate by 0.25% : Interest Rates Will Decrease : Comprehensive Guide
Repo Rate Reduction : The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has announced a significant cut in the repo rate, reducing it by 0.25 percentage points to bring it down to 6.25%. This marks the first reduction in interest rates in five years, signaling a shift in the central bank’s monetary policy.
Table of Contents
The decision is aimed at lowering the cost of borrowing, thereby stimulating economic growth and making credit more affordable for businesses and individuals.
Significance of the Repo Rate Cut

The repo rate is the interest rate at which commercial banks borrow funds from the RBI. A reduction in this rate lowers borrowing costs for banks, allowing them to offer loans at lower interest rates to businesses and consumers. This move is expected to have a cascading effect on various sectors of the economy, particularly those dependent on credit, such as housing, automobile, and agriculture.
Rationale Behind the Decision
The RBI’s decision to cut the repo rate comes at a time when economic growth is picking up. The central bank has revised the country’s growth estimate for the current fiscal year from 6.6% to 6.7%, reflecting positive economic momentum.
Also Read : Car Loan Tips For You : 10 Crucial Things to Know Before Getting a Car Loan!
Additionally, inflation remains a key concern, but the RBI aims to maintain it at around 4.2%. RBI Governor Sanjay Malhotra has expressed optimism that inflation will continue to decline in the coming months, allowing for further monetary policy adjustments if necessary.
Impact on Loans and Borrowers
The immediate impact of the rate cut will be seen in the form of reduced interest rates on loans that are linked to the repo rate. Borrowers will experience a decrease in their Equated Monthly Installments (EMIs) for various types of loans, including:
- Home Loans: Lower interest rates will make housing loans more affordable, encouraging more individuals to invest in real estate.
- Auto Loans: The cost of financing vehicles will decrease, potentially boosting demand in the automobile sector.
- Education Loans: Students and parents taking loans for higher education will benefit from reduced repayment burdens.
- Agricultural Loans: Farmers seeking credit for crops and equipment purchases will find borrowing cheaper, supporting the agricultural economy.
Historical Context and Policy Direction

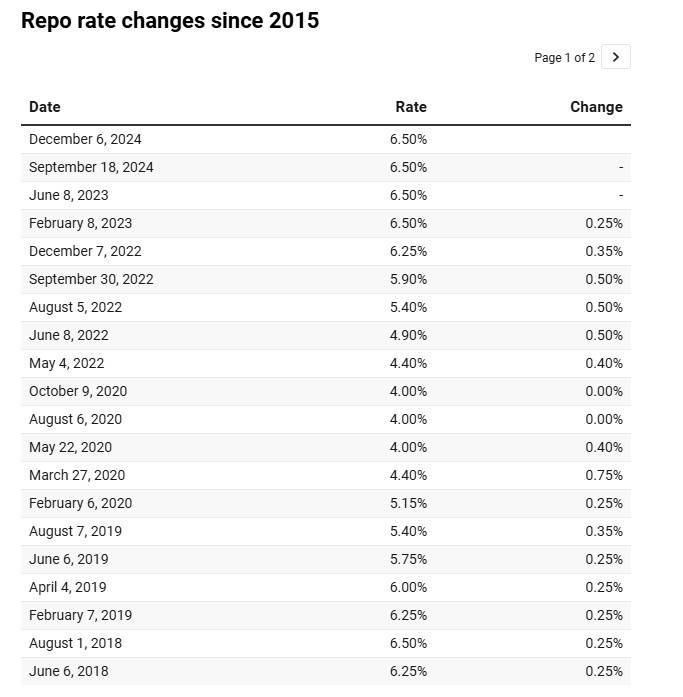
The last time the RBI cut interest rates was during the COVID-19 pandemic in May 2020, when emergency measures were taken to support the economy. Since then, the repo rate had been gradually increased in phases, reaching 6.50% as the RBI aimed to control inflation and stabilize the financial system. This latest rate cut signals a potential shift in policy focus towards supporting economic expansion rather than solely curbing inflation.
Monetary Policy Committee and New Leadership
The decision to cut the repo rate was made during the first monetary policy meeting under the leadership of newly appointed RBI Governor Sanjay Malhotra, who previously served as the Union Revenue Secretary. Notably, five of the six members of the Monetary Policy Committee (MPC) are new appointees. This suggests a fresh perspective in policy-making, with an emphasis on balancing growth and inflation control.
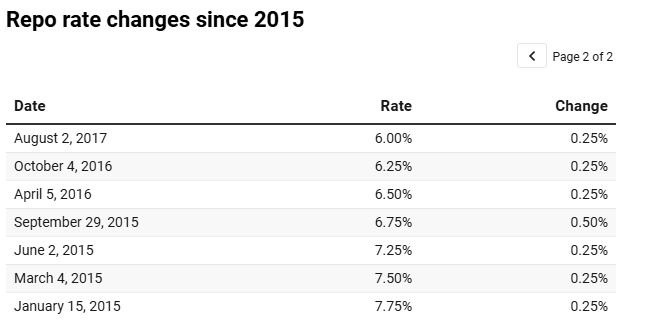
Repo Rate Reduction – Conclusion

The RBI’s decision to cut the repo rate by 0.25 percentage points is a strategic move aimed at boosting economic growth by reducing borrowing costs. The immediate benefits will be felt by borrowers across multiple sectors, while businesses may also experience a revival due to easier access to credit.
Buy Now : 200+ Premium Trading Courses
As inflation is expected to remain under control, further rate cuts in the future cannot be ruled out. This policy shift reflects the central bank’s commitment to fostering a stable and growing economy in the coming years.



